Picture the scene: a coffee shop, an airport terminal, or a quiet spot away from the office. Your laptop's battery icon turns red. Panic sets in as a deadline looms. A portable power bank offers a modern solution to this common anxiety. You just need the correct equipment. Today, we'll explain the technology, detail how to select the right device, and show how to power your laptop safely and efficiently.
Why Your Old Phone Power Bank Won't Work: The Magic of USB-C Power Delivery (PD)
Many people own a power bank for their phone. It is a surprise when that same device fails to charge a laptop. The reason is a fundamental difference in power requirements and technology.

The Power Gap Explained
Traditional power banks with older USB-A ports were designed for small electronics. These ports deliver a low amount of power, typically between 2.5 watts and 12 watts. In contrast, an average laptop requires much more electricity to charge its large battery. Standard laptops consume between 30 watts and 70 watts, while high-performance models can demand over 100 watts. This large difference in wattage is the power gap. A standard phone charger simply cannot supply enough electricity. At best, it might slow down how fast the laptop's battery drains.
Introducing USB-C Power Delivery (PD)
USB Power Delivery (PD) is the technology standard that solves this power problem. It operates through the modern, oval-shaped USB-C connector. USB PD is more than just a power source; it is an intelligent communication system. The power bank and the laptop talk to each other. They negotiate the fastest and safest charging speed possible. The technology has evolved over time. The latest version, USB PD 3.1, can deliver up to 240W of power, which is more than enough for any laptop on the market today.
Power Output Compared
The difference in power output between the old and new standards is significant. A direct comparison shows the technological leap. Legacy USB-A ports provide a power output in the 5W to 12W range. A USB-C port with Power Delivery, however, supports multiple high-power profiles, such as 45W, 65W, and 100W, specifically for laptops. Trying to charge a laptop with a USB-A port is like trying to fill a bathtub with a drinking straw. Using a USB-C PD port is like using a fire hose. The technology was developed in direct response to requests from laptop manufacturers who needed a more powerful connector for their increasingly demanding devices. This shift has helped consolidate the charger market, reducing electronic waste with a single-cable solution for all devices, a trend now supported through government regulations.
| Port Type | Typical Max Power Output |
| USB-A (Standard) | 5W - 12W |
| USB-C with Power Delivery (PD) | Up to 100W+ (with profiles at 45W, 65W, etc.) |
6 Key Specs of a Laptop Power Bank
When you shop for a laptop power bank, the packaging presents many technical terms. Understanding four key specifications—output power, capacity, ports, and safety features—will empower you to choose the right device.
Output Power (Wattage): The Most Important Number
Wattage (W) is the most critical specification for a laptop power bank. A power bank with insufficient wattage will fail to charge a laptop, even if it has a very large battery capacity. To find your laptop's required wattage, look at the original AC adapter. It will have "output" information printed on it, such as "20V / 3.25A". You can calculate the wattage with a simple formula: Watts = Volts × Amps. In this example, 20 multiplied by 3.25 equals 65W. As a general rule, smaller laptops and ultrabooks need 45W to 65W. Larger, high-performance models require 65W to 100W. The power bank's output must meet or exceed this number.
Battery Capacity: Understanding mAh vs. Wh
Power bank capacity is measured in two different units: milliamp-hours (mAh) and watt-hours (Wh). The distinction is important. Milliamp-hours measure electric charge, but this figure can be misleading because it does not include voltage. Watt-hours measure total energy, which is a more accurate indicator of a power bank's true capacity. Watt-hours provide a standard unit for comparing different power banks fairly. You can convert mAh to Wh with the formula: Wh=(mAh×V)/1000. The voltage (V) for most internal lithium-ion cells in power banks is 3.7V.
The 100Wh Travel Rule
For air travel, understanding watt-hours is crucial. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and other international bodies have strict safety rules for lithium-ion batteries. Power banks must be in carry-on luggage only; they are forbidden in checked bags due to fire risk. The capacity of each battery is limited to 100 watt-hours. This is why a 100wh power bank is a popular choice for travelers. Many manufacturers design their largest travel-friendly models to have a capacity of around 27,000 mAh, which converts to just under the 100Wh limit.
mAh Capacity |
Wh Equivalen,t (at 3.7V) |
Airline Compliance |
10,000 mAh |
37 Wh |
OK for Carry-on |
20,000 mAh |
74 Wh |
OK for Carry-on |
27,000 mAh |
99.9 Wh |
OK for Carry-on (at the limit) |
40,000 mAh |
148 Wh |
Requires Airline Approval |
Port Configuration for Maximum Versatility
An ideal laptop power bank offers a flexible port configuration. It must have at least one USB-C PD port capable of delivering the wattage your laptop needs. A good model will also include one or more USB-A ports. These extra ports are useful for charging other devices like a phone, headphones, or a smartwatch at the same time. The main USB-C port should also support high-wattage input. This allows the power bank itself to be recharged quickly.
Smart and Safe Charging Features
Modern power banks are no longer simple batteries; they are sophisticated electronic devices. Many now include a smart digital display. This screen shows the precise battery percentage remaining, the current power output in watts, and an estimate of the time left to charge or discharge. This is much more informative than a few blinking LED lights. Additionally, reputable power banks contain advanced safety systems. These circuits protect against overcharging, short circuits, and overheating. These features are vital for protecting both the power bank and your expensive laptop.
Recharging Speed: Powering Up the Power Bank
A high capacity power bank for laptop can store a lot of energy. Recharging it can take a long time with a weak wall adapter. Look for a power bank that supports fast input charging, such as 65W or 100W. A device that can recharge itself in just a couple of hours is much more practical than one that needs to be plugged in overnight. To achieve these fast speeds, you will need to use a powerful wall charger, like the one that came with your laptop. When choosing, prioritize power banks that feature "fast recharge" or "dual-way fast charging," as these are designed with advanced input circuits to safely handle higher wattages, saving you hours of downtime between uses.
How to Charge Your Laptop Safely and Efficiently

Owning the right laptop power bank is the first step. Following a few best practices for charging will protect your equipment, maximize efficiency, and extend the lifespan of both your laptop and power bank.
Using the Right Gear
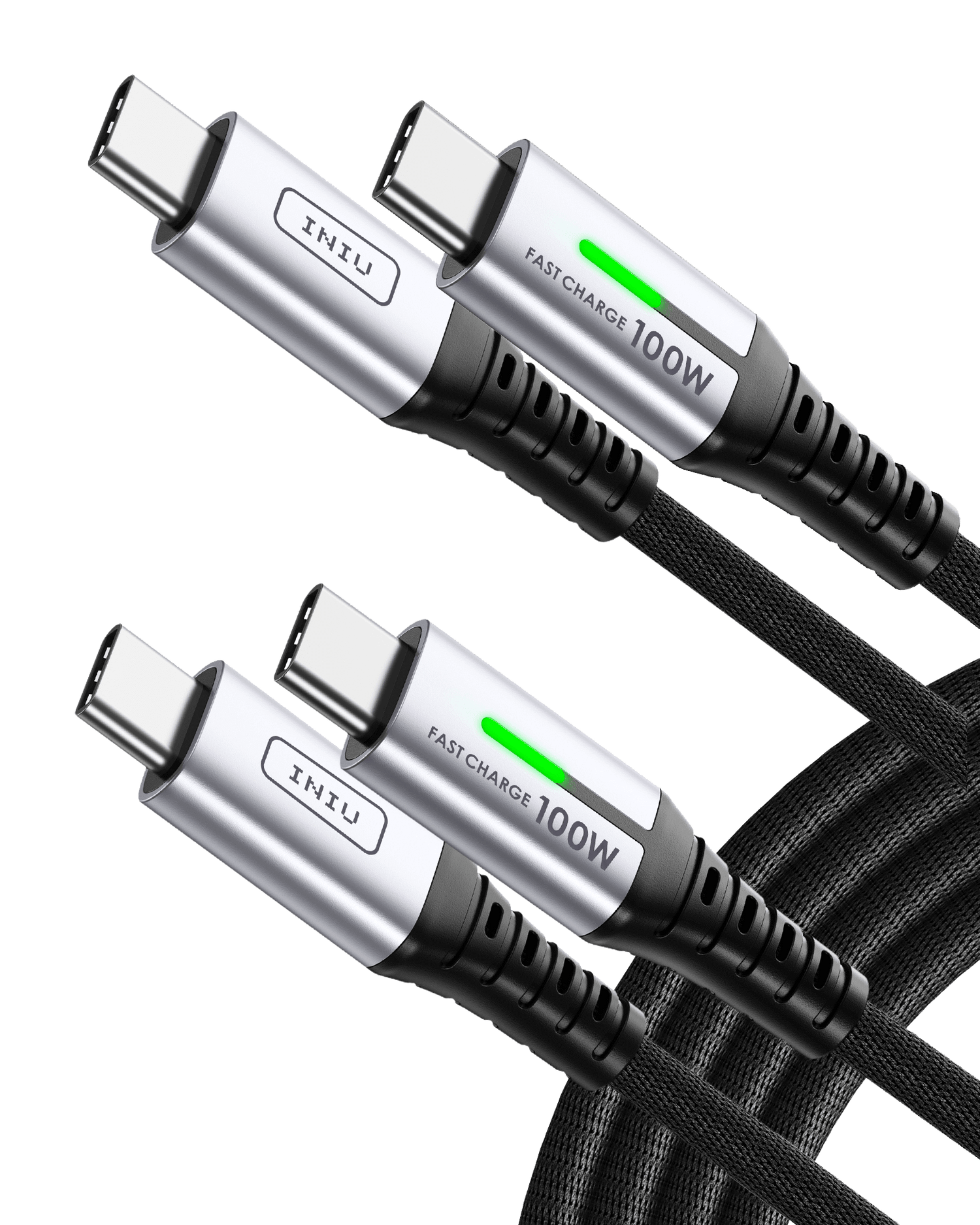
The USB-C cable is a critical part of the charging system. For charging at speeds above 60W, the cable must contain a special "E-Marker" chip. This chip communicates the cable's power-handling capabilities to the power bank and the laptop. If you use a standard, unrated cable for high-wattage charging, the system will default to a much slower speed as a safety precaution, or it may not work at all. Always use the cable provided with your power bank or a high-quality replacement that is explicitly rated for 100W.
Best Practices for Charging
For the quickest charge, connect the power bank when the laptop is asleep or turned off. This allows all the energy to go directly into the battery. If you need to work while charging, reduce your laptop's power consumption. Dim the screen's brightness and close any applications you are not using. High-wattage charging generates heat, which can degrade batteries over time. Place both the power bank and the laptop on a hard, flat surface like a desk. Avoid soft surfaces like a bed or sofa that can block airflow and trap heat. For long-term battery health, try to keep the charge level between 20% and 80%.
Pass-Through Charging Explained
Some power banks offer a feature called pass-through charging. This lets you charge a device from the power bank while the power bank itself is being charged from a wall outlet. It is a convenient feature when you have limited outlets, for instance in a hotel room. You can charge both your laptop and the power bank with a single wall adapter. This process, however, can create extra heat inside the power bank. Frequent use of pass-through charging may reduce the power bank's long-term lifespan.
Why Won't My Power Bank Charge My Laptop?
You have connected your new laptop power bank, but nothing is happening, or the charging is incredibly slow. Before assuming the device is broken, run through this simple troubleshooting checklist to identify the common culprits.
5 Common Culprits and Quick Fixes
A logical, step-by-step diagnostic process can often solve the problem quickly. Start with the most common and simplest issues first.
- Check the Cable and Ports: The cable is a frequent source of problems. Confirm it is rated for the power your laptop needs. Check that it is plugged in securely at both ends. If possible, try a different cable that you know works. Also inspect the USB-C ports on both the power bank and the laptop. They should be clean and free of any dust or debris.
- Verify Power Compatibility: Double-check the specifications. Are you using the correct high-wattage output port on the power bank? Some models have multiple ports with different power ratings. Does the power bank's wattage output meet or exceed your laptop's requirement? The information is printed on both devices.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature. If the power bank is very hot or cold, its internal safety circuits may temporarily prevent it from charging. Let the device return to room temperature before trying again.
- Check the Laptop: Not all USB-C ports on laptops support charging. Look for a small charging symbol or consult your laptop's manual. Sometimes, a simple reboot of the laptop can fix software-related power management issues.
- Reset the Power Bank: If a power bank detects a fault, it might enter a protective shutdown mode. Many models can be reset. The procedure often involves holding the power button for 10-15 seconds or connecting the output port to the input port with a cable for a short time.
How to Choose the Best Power Bank for Your Laptop
Now that you understand the technology and features, selecting the best laptop power bank is a straightforward process. It involves matching the device's specifications to your laptop's needs and your personal usage patterns.
Step 1: Determine Your Laptop's Wattage
The first and most important step is to identify your laptop's power requirement in watts. Check the original AC adapter that came with your laptop. This number is the minimum output wattage your power bank must provide. This is a non-negotiable starting point for your search.
Step 2: Decide on Capacity Based on Your Needs
Next, choose a capacity that fits your typical use. If you just need enough power for one full recharge of your laptop, a power bank with a capacity around 20,000mAh (about 74Wh) is a great starting point for most standard laptops and ultrabooks. For longer trips, multiple charges, or for powering other devices, a high capacity power bank for laptop near the 100Wh airline limit (around 27,000mAh) offers the most flexibility.
Step 3: Consider Portability and Use Case
There is a direct trade-off between battery capacity and physical size. A higher capacity requires more battery cells, which results in a heavier and bulkier device. Your lifestyle should guide your choice. A daily commuter might prefer a lighter 20,000mAh model for emergencies. A frequent traveler or remote worker will get more value from a larger 27,000mAh model that maximizes power while staying within travel regulations. A creative professional or gamer who needs to power a very demanding machine should prioritize the highest wattage (100W or 140W) and accept the larger size. At the 140W level, USB-C PD 3.1 allows full-speed charging for laptops, delivering desktop-class power through a portable power bank.
| Laptop Type | Typical Wattage Needed | Recommended Power Bank Output | Recommended Capacity (1-1.5 Charges) |
| Ultrabook / Chromebook | 45W - 65W | 65W+ | 20,000mAh - 27,000mAh (~74-100Wh) |
| High-Performance Laptop | 65W - 100W | 100W+ | 20,000mAh - 27,000mAh (~74-100Wh) |
| High-Performance Professional Laptop | 100W+ | 140W+ | 27,000mAh+ (~100Wh+) |
Power Up Your Productivity: Find Your Perfect Laptop Power Bank
Charging a laptop with a portable power bank is both possible and practical. The key is knowledge. You must match the power bank's wattage to your laptop's needs, choose a capacity measured in watt-hours that suits your lifestyle, and use high-quality, properly rated cables. With the right laptop power bank, you gain the freedom to work, create, and connect from anywhere, completely independent of wall outlets. Your productivity is no longer tied to a power cord.
FAQs
Q1: What does the 100Wh airline limit mean in mAh?
A: The 100Wh limit set by the FAA and other air travel authorities is equivalent to approximately 27,000mAh, assuming a standard internal battery voltage of 3.7V. This is why many of the largest travel-friendly power banks have this specific capacity.
Q2: Can I use my phone's power bank for my laptop?
A: It is extremely unlikely. Standard power banks for phones typically have a low power output of 5W to 18W, though some newer fast-charging models may go a bit higher. Laptops require a much higher output, usually 45W or more, which only a dedicated laptop power bank with USB-C Power Delivery can provide. High-power power banks are designed to charge both phones and laptops, intelligently distributing output based on the device's requirements.
Q3: How many times can a 25,000mAh power bank charge my laptop?
A: This depends on the battery size of your laptop. A 25,000mAh power bank holds about 92.5Wh of energy. After accounting for energy loss during the charging process (usually 30-40%), it can provide one full charge to a laptop with a 70-80Wh battery.
Q4: Is it safe to leave my laptop charging from a power bank overnight?
A: Yes. Both modern laptops and quality power banks have built-in safety systems that prevent overcharging. The power flow will stop automatically once the laptop's battery is full. For the absolute best long-term health of the battery, however, it is good practice to disconnect devices once they are charged.
Q5: How long will a laptop power bank last?
A: A high-quality power bank, with proper care, should last for several years. Like the battery in your laptop, its ability to hold a full charge will gradually decrease over time. You can typically expect it to perform well for 300 to 500 full charge-and-discharge cycles before the degradation becomes significant.